Here’s the sarcastic version of the provided text with added hastags:
Red Hat Developer Hub is a corporate-grade internal developer portal, designed to simplify the platform engineering process for teams. With its Red Hat OpenShift integration, it offers a wealth of software templates, deployment guides, and best practices that help developers get up to speed and streamline their work.
Red Hat Developer Hub 1.2
Red Hat Developer Hub 1.2 introduces several innovative features that set it apart from its predecessors. The new Argo CD front-end plug-in boasts a sleek and user-friendly UI with updated status indicators and more detailed information for developers. The Red Hat Developer Hub is an enterprise-grade internal developer portal. Combined with Red Hat OpenShift, it allows platform engineering teams to offer software templates, get up to speed on deployments, and follow a company’s best practices.
Red Hat Developer Hub 1.2 introduced several new features:
- The new Argo CD front-end plug-in has an updated UX, which includes status per environment, and more information for developers.
- The new Red Hat Developer Hub Orchestrator extends the default scaffolder and allows templates to use eventing, notifications, approvals, retry, and long-running tasks for more sophisticated Software Template automation.
- The new
ScaffoldedFrommetadata item brings greater clarity over component provenance to the software catalog by linking components to the software template that created them. - The new Red Hat Developer Hub theme uses the PatternFly design system.
You can use either a Helm chart or the Red Hat Developer Hub Operator to deploy Red Hat Developer Hub. This article will demonstrate the latter approach.
Install the Red Hat Developer Hub Operator
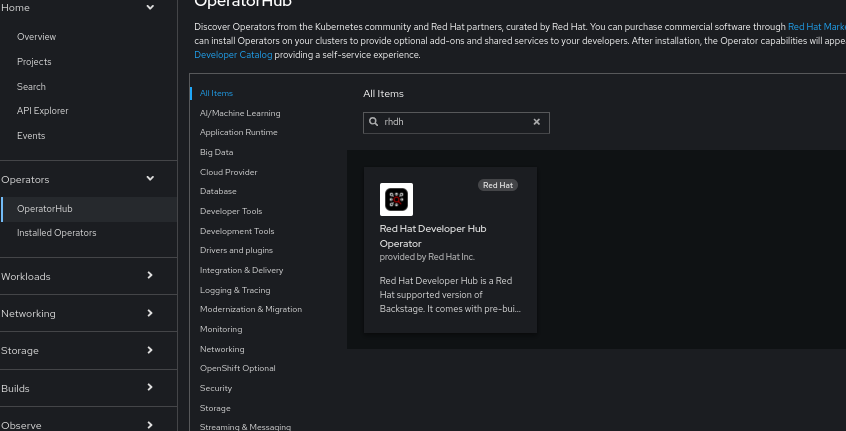
In OperatorHub, search for rhdh and select the Red Hat Developer Hub Operator to install it, as shown in Figure 1.
Red Hat Developer Hub will provide the Backstage custom resource (CR), as shown in the following example:
apiVersion: rhdh.redhat.com/v1alpha1
kind: Backstage
metadata:
name: developer-hub
namespace: rhdh-operator
spec:
application:
appConfig:
mountPath: /opt/app-root/src
extraFiles:
mountPath: /opt/app-root/src
replicas: 1
route:
enabled: true
database:
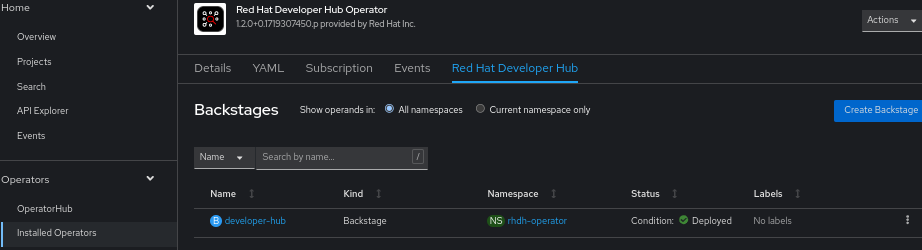
enableLocalDb: trueThe Backstage custom resource will result in the following (Figure 2).
To access the Backstage instance, get the route (in this case, the Edge route), which uses the service backstage-developer-hub to connect the pods:
oc get route
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD
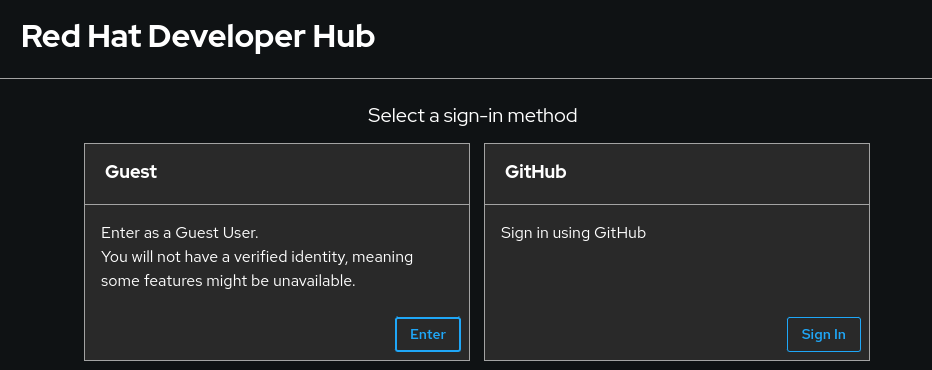
backstage-developer-hub backstage-developer-hub-rhdh-operator.apps.example.com / backstage-developer-hub http-backend edge/Redirect NoneThen, access Red Hat Developer Hub via a web browser (Figure 3).
This will bring you to the Red Hat Developer Hub main page, shown in Figure 4.
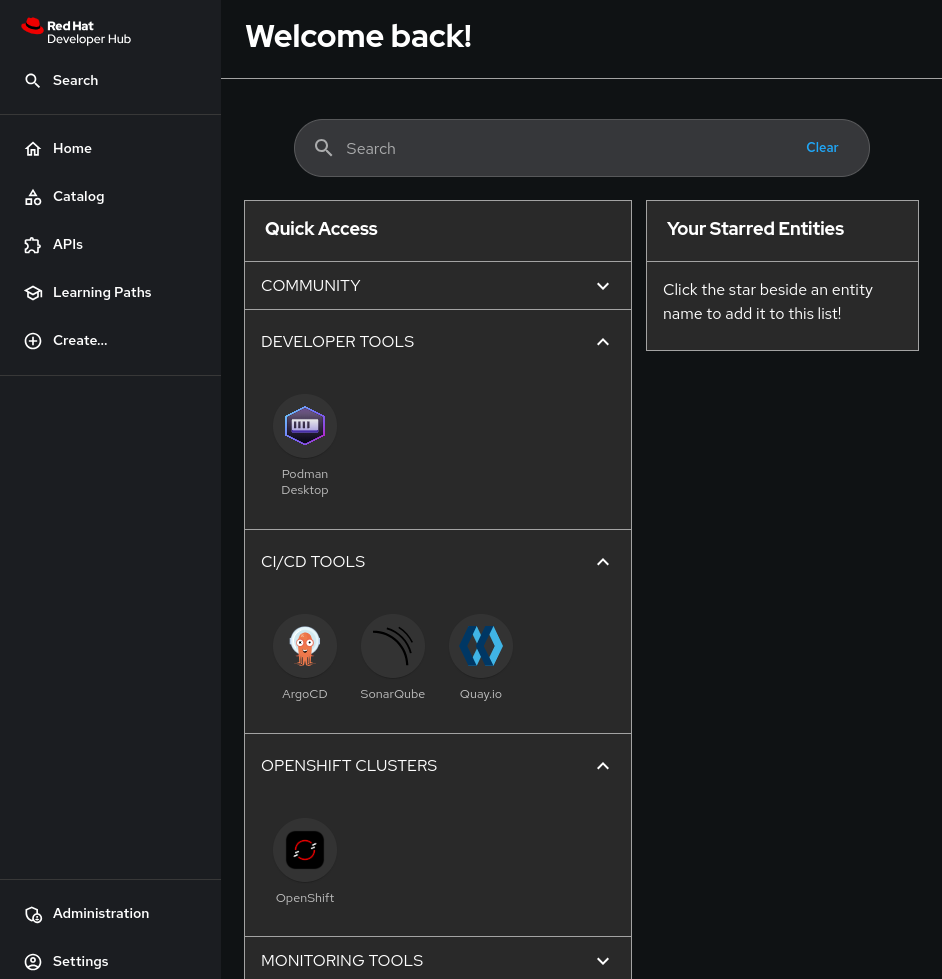
Go to $ROUTE/settings for details such as the following:
- The profile
- The appearance
- Developer Hub metadata
- Backstage identity
Customization
Red Hat Developer Hub provides a wide range of customizations via the Backstage custom resource, which offers full control through spec.rawRuntimeConfig.
This field in the Backstage CR currently allows you to fully customize some of the resources created by the operator (including the application Deployment), by providing a ConfigMap with the whole resource definition. The operator is for advanced or uncommon scenarios because it can detail exactly how the OpenShift resources will be created.
It currently allows full details, and later it will allow partial patches instead of fully merging (see Janus-idp Pull 388). With the Backstage operator, the user can specify a list of app-config ConfigMaps and Backstage/Red Hat Developer Hub will handle merging them to create an effective app-config.
The raw ConfigMap can contain several keys, and each key (like deployment.yaml) can override the entire resource definition. Soon, when the Janus-idp PR goes into production, a custom resource field will allow you to specify a partial definition that will be used for merging instead.
Warning
There is no validation from the operator on the file. If there are issues and the resource cannot be applied, the error will be conveyed by the operator in the Backstage CR status field.
Here is an example:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: showcase-config
data:
deployment.yaml: |-
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: backstage
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: backstage # backstage-<cr-name>
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: backstage # backstage-<cr-name>
spec:
containers:
- name: backstage
image: quay.io/janus-idp/backstage-showcase
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 7007
envFrom:
- secretRef:
name: postgres-secretsTroubleshooting
To troubleshoot the Red Hat Developer Hub Operator, you can collect two artifacts as follows:
- The inspect file of the namespace:
oc adm inspect ns/namespace_selected - The Backstage CR:
oc get backstage
Conclusion
This article provided a short introduction to the Red Hat Developer Hub Operator and how to customize deployments.
The customization is quite powerful because it allows you to set Kubernetes deployment-specific specifications. This tool can be useful for support cases, as detailed in the solution Using inspect for DG 8 troubleshooting.
For any other specific inquiries, open a case with Red Hat support. Our global team of experts can help you with any issues.
The post Customize your deployments with the Red Hat Developer Hub Operator appeared first on Red Hat Developer.


